Abstract
Introduction:Wilms tumor 1 messenger RNA (WT1mRNA) is detected in patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS), and is reportedly a useful minimal residual disease (MRD) marker. Allogeneic stem cell transplantation (allo-SCT) is the established cellular immunotherapy with a graft-versus-leukemia (GVL) effect and eliminates residual leukemia cells via the alloimmune response. The GVL effect is generally considered to occur after immune reconstruction. Therefore, the predictive power of WT1mRNA as an MRD marker for relapse may differ between the early and late periods after allo-SCT because the GVL effect is not expected in the early period without enough immune reconstruction. However, no studies have reported whether the predictive power of WT1mRNA for relapse changes in a time-sequential manner after allo-SCT. Hence, we investigated the relationship between WT1mRNA as a time-dependent variable and days after allo-SCT for AML/MDS relapse using a dynamic landmarking approach, and developed a dynamic relapse prediction model using the WT1mRNA level and measurement timepoint after allo-SCT.
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed AML and MDS patients who received allo-SCT at Osaka Metropolitan University Hospital, and whose WT1mRNA levels were measured at least once from January 2008 to April 2021. WT1mRNA levels in peripheral blood were measured using an "Otsuka" WT1mRNA assay kit (Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.). Relapse was defined as hematological relapse or salvage chemotherapy intervention and/or donor lymphocyte infusion. To evaluate time-sequential changes in the predictive power of WT1mRNA for relapse and to develop a dynamic relapse prediction model, dynamic landmarking analysis was performed, which was reported by Hans C. van Houwelingen et al. The probabilities of the 1 year cumulative incidence of relapse (CIR) post-landmark timepoint were estimated with the Kaplan-Meier method. The Cox proportional hazard regression model was used to calculate the time-sequential hazard ratio for 1 year CIR not only post-landmark but also post-any timepoints after allo-SCT, and to develop a dynamic relapse prediction model. p < 0.05 was considered significant.
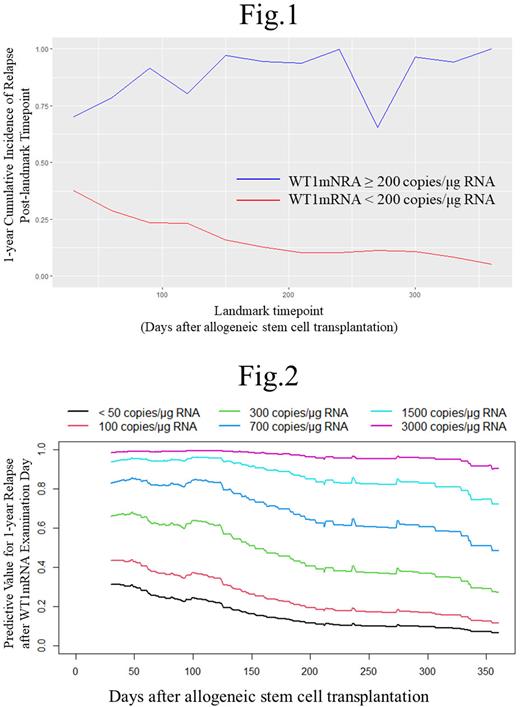
Results: We analyzed 265 patients (AML: 197 and MDS: 68) and 2,539 WT1mRNA tests. Median patient age was 46 years, 55% of patients achieved complete remission at the time of allo-SCT, and the 2 year relapse-free survival rate was 46%. First, patients were divided into two groups, namely, those with WT1mRNA levels higher and lower than 200 copies/μg RNA, which is a previously reported cutoff value. Figure 1 shows a summary plot of the 1 year CIR of the two groups post-landmark timepoint. The 1 year CIR decreased over time after allo-SCT in the lower WT1mRNA group but not in the higher WT1mRNA group. The difference in 1 year CIR between the two groups increased over time after allo-SCT. Moreover, the hazard ratio of log WT1mRNA levels for 1 year CIR post landmark timepoints after allo SCT increased over time, and there was a significant interaction between WT1mRNA levels and landmark time (p < 0.001). These findings indicate that the predictive power of WT1mRNA levels for relapse increases over time after allo-SCT. Second, we developed a dynamic relapse prediction model that can predict the 1 year CIR post-any timepoint after allo-SCT based on individual post-transplant WT1mRNA levels and measurement timepoints. Figure 2 shows a time series of predictive values for 1 year relapse post-any timepoints derived from this prediction model, which assumed that WT1mRNA levels remain constant over time after allo-SCT.
Conclusions: We demonstrated that the predictive power of peripheral blood WT1mRNA for relapse increases after allo-SCT over time. This finding implies that MRD in the early phase after allo-SCT is more likely to disappear owing to the GVL effect after immune reconstruction compared to one in the late phase. Transplant clinicians should pay attention to the difference in predictive power for relapse depending on the period when they observe elevated WT1mRNA levels. Dynamic landmark analysis also enabled prediction of continuous 1 year CIR post-any timepoint after allo-SCT by inputting the individual WT1mRNA level and measurement timepoint. Dynamic relapse prediction will offer useful information for clinical decision making.
Disclosures
Okamura:Mitsubishi Research Institute: Honoraria; NIPPON SHINYAKU CO.,LTD.: Consultancy, Honoraria; AstraZeneca K.K.: Research Funding. Yokota:AstraZeneca: Speakers Bureau; Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.: Speakers Bureau; Nihon Medi-Physics: Research Funding. Umemoto:Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.: Honoraria; Kyowa Kirin Co., Ltd: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria. Makuuchi:CSL Behring: Research Funding; Asahi Kasei Corporation: Honoraria. Takakuwa:Sanofi K.K.: Consultancy, Honoraria; ONO PHARMACEUTICAL CO., LTD.: Honoraria; AbbVie GK: Research Funding; Fujimoto Pharmaceutical Corporation: Honoraria; Janssen Pharmaceutical K.K.: Honoraria; Bristol-Myers Squibb Comapany: Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria; Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.: Honoraria; Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited.: Honoraria; Kyowa Kirin Co., Ltd: Honoraria; Celgene Corporation: Research Funding; Incyte Corporation: Research Funding; Perseus Proteomics Inc: Research Funding; GSK plc: Research Funding. Nishimoto:CSL Behring: Honoraria; Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.: Honoraria; Kyowa Kirin Co., Ltd: Honoraria; Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited.: Honoraria; Janssen Pharmaceutical K.K.: Honoraria; Astellas Pharma Inc.: Research Funding; Bayer: Research Funding; Pfizer Japan Inc.: Research Funding; ZENYAKU KOGY Zenyaku Kogyo Co., Ltd.: Research Funding. Nakamae:VERITAS Corporation: Research Funding. Nakashima:SymBio Pharmaceuticals Limited: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.: Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding; Amgen Inc: Honoraria; Janssen Pharmaceutical K.K.: Honoraria; Astellas Pharma Inc.: Research Funding; Pfizer Japan Inc.: Research Funding; AbbVie GK: Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb Comapany: Research Funding; Celgene Corporation: Research Funding. Koh:NIHON PHARMACEUTICAL CO., LTD: Honoraria; MSD K.K: Honoraria; Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma Co., Ltd.: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria; Asahi Kasei Corporation:: Honoraria; Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited.: Consultancy, Research Funding; Amgen Inc: Research Funding; AstraZeneca K.K.: Research Funding. Hino:Meiji Seika Pharma Co., Ltd.: Honoraria; CSL Behring: Honoraria; MDS K.K: Honoraria; Astellas Pharma Inc.: Honoraria; AstraZeneca: Honoraria; AbbVie GK: Honoraria; Eisai Co., Ltd: Honoraria; Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.: Honoraria, Research Funding; ONO PHARMACEUTICAL CO., LTD.: Honoraria; Kyowa Kirin Co., Ltd: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Sanofi K.K.: Honoraria; Celgene Corporation: Honoraria, Research Funding; Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma Co., Ltd.: Honoraria, Research Funding; Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited.: Honoraria, Research Funding; Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.: Honoraria, Research Funding; Japan Blood Products Organization: Research Funding; NIPPON SHINYAKU CO.,LTD.: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria; Pfizer Japan Inc.: Honoraria, Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb Comapany: Honoraria; Janssen Pharmaceutical K.K.: Honoraria; DAIICHI SANKYO COMPANY, LIMITED.: Consultancy, Research Funding; JCR Pharmaceuticals Co., Ltd.: Research Funding; SEKISUI MEDICAL CO., LTD.: Research Funding; KM Biologics: Honoraria; TAIHO PHARMACEUTICAL CO., LTD.: Research Funding; TEIJIN PHARMA LIMITED.: Research Funding; Asahi Kasei Corporation:: Research Funding; Labcorp Drug Development: Research Funding. Nakamae:DAIICHI SANKYO COMPANY, LIMITED.: Honoraria; Amgen Inc: Honoraria; Janssen Pharmaceutical K.K.: Honoraria; CMIC HOLDINGS Co., Ltd: Research Funding; NIPPON SHINYAKU CO.,LTD.: Honoraria; Alexion: Research Funding; Simon-Kucher & Partners: Consultancy; ONO PHARMACEUTICAL CO., LTD.: Consultancy; Bristol-Myers Squibb Comapany: Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding; Meiji Seika Pharma Co., Ltd.: Research Funding; Astellas Pharma Inc.: Honoraria; Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.: Honoraria; Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma Co., Ltd.: Honoraria; Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited.: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal